Holding an American university degree opens up many opportunities for building a successful career in the future. That is why nearly a million international students come to the “land of opportunity” every year. The first thing they need to know to successfully complete the quest of obtaining the desired diploma is the exact answer to the question: “What is the American University credit system?” After all, it is the basis of higher education in the United States.
If you are a prospective foreign learner who is a bit confused and concerned about what to expect while studying in the US, you have come to the right place at the right time. All the answers are waiting for you below.
Semester Hours vs. Contact Hours: What’s the Difference?
For you to have a complete understanding of the American university credit system, let us begin with the basics: “How many semesters are in a college year in the US?” The answer is pretty simple — there are only two of them. During your studies at school, you’ll need to learn how to distinguish between semester hours and contact hours. As an international student, this may be difficult to grasp at first. So here’s a little cheat sheet to help you understand how many credits to graduate college you need:
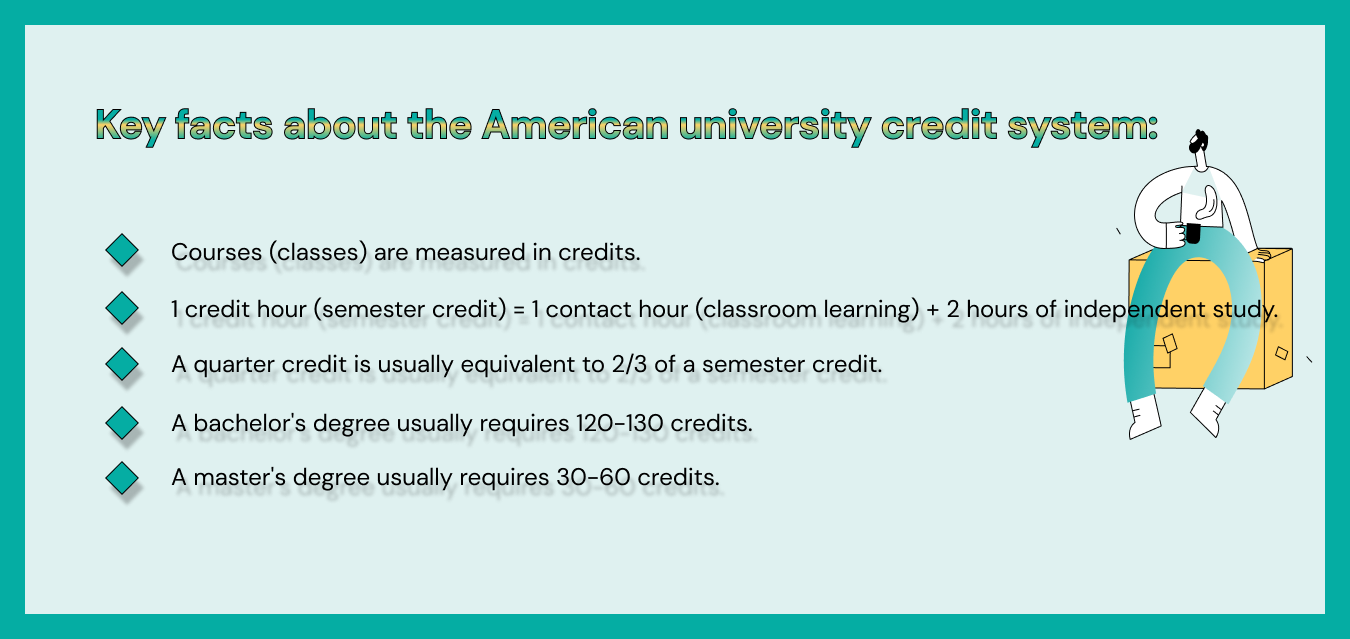
Semester hours and credit hours are the same thing. Credit hours, or simply credits, make up your workload in one course. Each course has a certain number of semester (credit) hours to be completed. In turn, one credit hour is divided into contact hours and independent study hours.
For your convenience, memorize the following formula:
1 credit hour = 1 contact hour + 2 hours of independent study
We hope you understand the American university credit system better now. As for the definition of “contact hour,” everything is logical here. This is the time a learner spends with the professor at lectures or labs. Accordingly, independent preparation is the student’s self-training for the class.
One semester hour is equal to 15-16 contact hours per semester, regardless of the length of the course.
Determining Credit Hours for Graduation
Now that we’ve discussed the basic concepts of semester and contact hours, it’s time to learn about another type of credit hours.
How many credits to graduate college: Understanding quarter credits
Although the previously mentioned estimates are the most typical, there are many universities that have a slightly different approach to measuring college workload. They use quarter hours because their academic year is divided into quarters rather than semesters. In this system, a quarter credit is typically equivalent to 2/3 of a semester credit. For example, a course worth three semester credits (credit hours) would be around five quarter credits in a quarter-based system.
The American university credit system: The role of credits in calculating GPA
We hope everything is clear to you so far because we are moving on. Credits play an undoubtedly important role in whether you receive your degree or not, but they are not the only ones. Every international student should also have a sufficient grade point average — or simply GPA.
All the grades you get when completing a particular credit (semester hour) affect your grade point average GPA. To calculate the points earned, the grade in each course is multiplied by the number of credit hours it contains. For example, an A in a three-credit course will have a greater value to your GPA than an A in a one-credit course.
Important! The cumulative GPA comes from dividing the total number of points earned by the total number of credits.
Earning the Necessary Credits for Your Degree in America
If you are an international student who is currently studying under the European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System (ECTS) and plan to transfer to an American university, you should know that they are not interchangeable.
How many credits is full time student? Converting European credits to American credits
In the ECTS system, credit hours are generally measured differently than in the American university credit system.
- European Credit Transfer System (ECTS). One ECTS credit is equal to approximately 25-30 hours of a student’s course load, including lectures, assignments, and individual work.
- American credits. The American university credit system measures credits in semester hours. As a rule, one semester hour is one hour of studying per week with a professor and two hours of preparation for class on your own during the semester.
Unfortunately, there is no direct and universal formula for converting ECTS credits to American credit hours. Typically, colleges equate ECTS academic hours to US academic hours based on course content, workload, and degree programs.
“Consultation with an academic advisor or the International Student Affairs Office at your university will help you better manage the ECTS conversion process.”
Leticia Adamson, PhD in English Literature and ESL Program Head at CustomWritings.com
Credit Requirements for Bachelor’s and Master’s Degrees
And so we come to the most important question: “How many credits do you need to graduate?” To give you a full answer, we need to delve into what degree you plan to graduate with. Most often, international students receive two types of diplomas from schools in the United States: a bachelor’s degree and a master’s degree. Each of them has different credit hour requirements.
Bachelor’s and Master’s degrees: How many credits to be a full time student and graduate on time?
The bachelor’s degree is a four-year undergraduate program offered at all universities and many colleges. Students complete a BS degree to gain in-depth knowledge in their chosen field of study. Many professional careers and higher-level positions require this kind of diploma.
Credit requirements: Usually, about 120-130 credits.
A master’s degree is a postgraduate program that follows the completion of a bachelor’s degree. It offers more advanced learning in a particular discipline compared to a BA program. If you are planning to earn a master’s degree, you should be prepared to dedicate one to three years of schooling to this pursuit.
Credit requirements: Typically, around 30-60 academic hours.
Thus, if you are wondering how many credits to be a full time student you need to take each semester, the answer is about 12-15. Predicting your next question, “How many classes is full time in college,” — we answer that it’s 4-5.
FAQ
- What is the American university credit system?
The credit system of American universities is a method of measuring a student’s academic workload and progress. The cornerstone of this system is the concept of “credits” or “semester hours.” One college hour is usually equal to one hour of classroom learning and two hours of self-preparation per week during the semester. A student needs to complete a satisfactory number of credits (academic units) to earn a degree. Each course has a different number of academic hours.
- How many credits are needed to graduate from a US university?
It all depends on what kind of diploma the person wants to graduate with. If their goal is a bachelor’s degree, they need to successfully complete 120-130 credit hours. In the case of postgraduate education (master’s degree), a student needs to focus on 30-60 credits to graduate.
- What is the difference between semester hours and contact hours?
Contact hours are a component of semester hours (credit hours/credits). This is the actual time a learner spends in class with a teacher. Contact hours include lectures, discussions, labs, or other educational activities.