The start of the new age intrigued the early Americans, and only a few envisioned economic prosperity and welfarism. However, agriculture and the local food movement increased, ushering in a new era.
Food and Agriculture Problems
While farming and the local food movement have succeeded in making civilization possible, it has yet to do much to protect against their collapse. Throughout history, the growth of agriculture has competed with population size, degradation of resources, climate change, and other factors that affect food supply.
Soil depletion tops the list of problems encountered by early farmers. Today, innovations like the pow (circa 3000 BCE) and irrigation (circa 6000 BCE) brought much gain to agriculture. However, the irresponsible use of these innovations caused a major problem for agriculture in the form of soil degradation, which is the building ground of agriculture. A lot of scholars and college students focus on the topic in their research papers. Many undergrads tend to hire a professional writer at a trusted research paper writing service to write the project and investigate the agriculture advent most concisely. This research digs deep into the advent of agriculture and the local food movement from the closure of the hunting-gatherer era.
Importance of Farming in America
Farming has proven important throughout American history because it can leave an indelible mark on the U.S. economy. A report from the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) stipulates that the food and agriculture sectors made a 10% share in the 2020 employment data, comprising nearly 20 million part-time and full-time jobs. Additionally, cash receipts from crops have totaled about $198 billion.
The mutual dependence of other sectors like transport, water, chemical, and energy systems with farming makes it a propelling force for the growth of the American economy. Agriculture has always had the potential to positively impact economic development in America, with a consistent contribution to the overall GDP (Gross Domestic Product).
Over the years, farming has done numerous good to American society through the instrumentality of farm production. The frequent production of plants, vegetables, and diverse crops throughout the country has made it easy for citizens to enjoy local food. Fishery and forestry activities are another important reason farming has been, and will continually be, crucial to the American economy. With the input of agriculture, the conservation of trees and forests for other use is possible. Throughout American history, growth can only be independently highlighted by counting farming activities.
History of Food Systems
The history of local foods in America grew from a reaction to the changes made to the food system in the 20th century. The crucial difference resulted from the rise of price support and subsidies for farm commodities. Support for farm produce began during the Great Depression to pacify family farms. This, however, led to the large purchase of agricultural commodities by big establishments to produce pre-packaged foods.
Progressively cheap farm commodities made it inexpensive to raise vast amounts of sustainable livestock between the 1970s and 1980s. As an indication of the growing local food movement, farmer’s markets in America increased from 1,755 to 8,669 between 1994 and 2016. This was called the “locavore” movement in 2007, coined by four San Francisco women in 2005, with the idea that people should exploit food products grown within 100 miles of their abode. Unlike other social movements, the locavore movement is driven by farmers and customers and the bond they share rather than conventional support organizations.
Agriculture in the past
The cultivation of food produced through farming has created an enormous supply. Agriculture has been thought to be practiced for more than 13,000 years, with broad establishment for 7,000 years. In the comprehensive view of history, this is just a fragment of existence compared to almost 200,000 years spent by our ancestors in hunting, scavenging, and gathering in the wild.
During the brief history of agriculture, there has been a radical transformation to American society and the world at large, fueling a global population that has expanded to over 7 billion since 10,000 BCE. The road to present-day agricultural practice has yet to be smooth. Farmers have been made to adapt to the numerous threats posed by natural forces.
As far back as 11,000 BCE, people have gradually transitioned from a gatherer and hunting lifestyle to crop cultivation and animal husbandry for food. This migration to agriculture is believed to have been adopted spontaneously in different parts of the world, comprising Central America, northern China, and the Fertile Crescent in the Middle East that held certain early civilizations.
Coming down to 6000 BCE, the widespread domestication of farm animals has taken prominence, as well as the adoption of agriculture in major continents, excluding Australia.
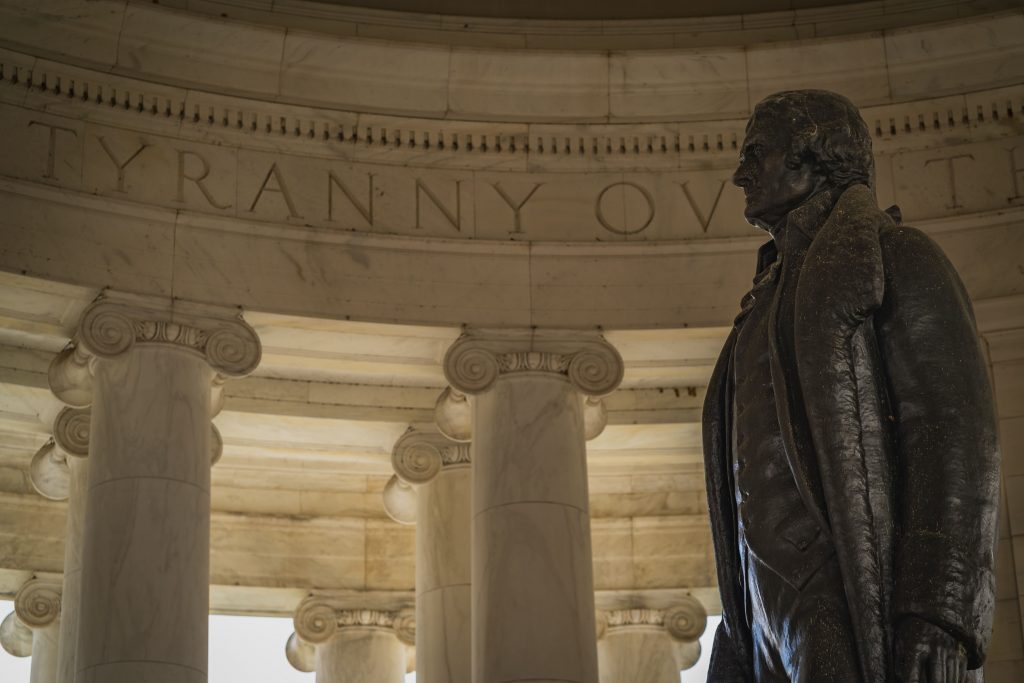
“Agriculture is our wisest pursuit because it will, in the end, contribute most to real wealth, good morals & happiness.” Thomas Jefferson, former president of America, 1801-1809
The New Farming Need
Since using modern equipment such as pesticides and fertilizers has increased crop yields, it has become a necessity for the farming community in America. At the same time, these have contributed to climate change, water, and soil pollution. To balance this, the local food and agriculture movement must alleviate the impact by subscribing to biodiversity.
Sustainable agriculture is one necessary factor to put into consideration. Through this, ranchers and farmers can be sure their lands will be of maximum profit while improving their soil fertility. Climate change regulation is another modern need of the farming community in America. Setting a system in place that will help to promote sustainable farming practices in the sector will provide help for agricultural adaptation. This will combat the greenhouse gas emissions produced by annual farming practices and address the possible challenges posed by climate change.
Provisions of agriculture innovation are another necessity for farming in America. Universal adoption of GPS technology, temperature-sensing devices, and machines for land surveys will greatly improve farming activities for better yield.
Pollan Omnivore’s Dilemma
The Pollan Omnivore’s Dilemma brings perspective to the broad range of food choices that we are faced with. This modern choice of food is done using four meals on a range, from processed to self-gathered, educating people on how the revolution in the agricultural industry has impacted our eating behavior.
The Pollan Omnivore’s Dilemma teaches what true natural food looks like and why organic food is not necessarily better. It also points to the options that we have to make between ethical, cheap, environmentally friendly, and sustainable meals.