Previously, in our first guide, we discussed 12 facts for research paper on child development, which, we are certain, acknowledged you with quality information.
In this guide, however, we will be focusing on 20 child development research paper topics, which are perfect if you are in a hurry and don’t want to waste your time looking for a good topic for your research paper.
Of course, you don’t want to forget reading our last guideline, writer’s manual for research paper on child development, which is perfect for polishing your research paper writing skills and improving the composition of your paper further.
20 Child Development Research Paper Topics
- How Children Change and Grow over the Course of First 12 Years
- Why Child Development was Largely Ignored Throughout the History
- The Social, Emotional and Cognitive Aspects of Child Development and Growth
- The Benefits of Studying How a Child Grows, Change and Learns Things.
- A Research Paper on the Forming of Ego in the Stages of Child Development
- A Research Study on Behavioral Child Development Studies
- Does Environment Really Play a Significant Role in Child Development?
- The Influence of Parents, Peers and Caregivers on the Development of a Child
- Why Child Development Plays a Vital Role in Shaping the a Person’s Entire Life
- The Reason behind the Children’s Active and Hands-on Experience Learning
- What Kind of Child Development Takes Place During Prenatal Stage?
- Are Children Really More Intelligent and Creative than Average Adults?
- Why Play is Significant in Helping Children Learn and Understand Life
- Why Speaking to a Real Person Is More Important for a Child’s Growth than Just Playing Games
- How a More Frequent Social Interaction can Help Babies Learn More and Faster
- Why Premature Babies are Vulnerable to Noise-Induced Hearing Loss?
- How Much Time Should Parents Spend With Children to Help Their Brain Develop?
- Can Music Increase Visual, Motor, Attention and Mathematical Skills of in Children?
- The Five Stages of Psychological Development in Children Explained
- The Four Kind of Parenting and The One You Should Adapt
When it comes to writing about complex topics like child development for a research paper you need to have a good grasp of the subject and a plan. But the complexity of the topic and the time required for research can be too much for students. That’s where a research paper writing service can help. These services provide papers written to your specifications and high quality content that meets academic requirements.
By using a research paper writing service you not only save time but also get guidance on how to present your ideas clearly. Whether you’re looking at cognitive, emotional or social development of child, professional research paper writing service can help you refine your research focus and deliver a well written and insightful paper. For students with multiple responsibilities this can be a lifesaver in achieving academic success.
Facts about Childhood Development Stages
Researchers and psychologists have dedicated extensive efforts to studying child development. Development encompasses various stages, each marked by unique milestones and growth patterns. Let’s swell deeper into interesting facts about child growth and development. There will also be more topics for research papers.
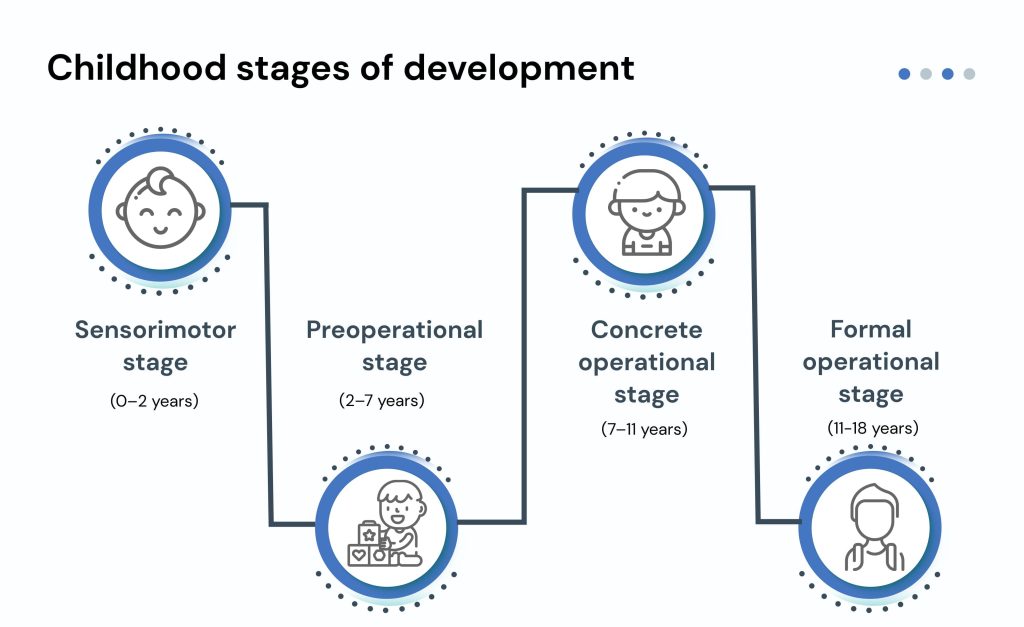
There are different views on the stages of children development. Jean Piaget and Erik Erikson are the most significant researchers. They contributed to the field of child development psychology. Piaget developed the following childhood stages of development.
- Sensorimotor stage (0–2 years)
- Preoperational stage (2–7 years)
- Concrete operational stage (7–11 years)
- Formal operational stage
Erik Erikson made up the following different stages of child psychological development.
- Trust vs. mistrust (birth to 12–18 months)
- Autonomy vs. shame & doubt (18 months to 3 years)
- Initiative vs. guilt (3 to 5 years)
- Industry vs. inferiority (5 to 12 years)
Yet, we will focus on the 4 broad definitions of these stages. They’re infancy and toddlerhood, early childhood, middle childhood, and adolescence. This information can serve for you as trigger for further exploration. You’ll be able to use it for your research paper about child development.
Infancy and Toddlerhood Stage
During the infancy and toddlerhood stages, children undergo remarkable child growth and development. It lays the foundation for their future. This period encompasses the first few years of a child’s life. It starts from birth until around the age of three.

- Rapid physical growth. Infancy and toddlerhood involve rapid physical changes. Babies double their birth weight within the first five months. By the age of two, their height increases by about 50%. This states every journal of early childhood research.
- Cognitive milestones. Toddlers have an extraordinary capacity for learning and cognitive development. During this stage, they begin to understand object permanence. Kids also understand the concept that objects continue to exist even when they are out of sight.
- Sensorimotor exploration. Infants explore their environment through their senses and motor skills. They enjoy manipulating objects, grasping, shaking, and banging them to understand their properties.
Early Childhood Stage
During the infancy and toddlerhood stage, children undergo remarkable child growth and development. It lays the foundation for their future. During this period, remarkable growth occurs. Children get new skills and knowledge. Facts about child development in this stage are the following:
- Rapid brain development. Significant brain development marks the early childhood stage. It is a critical period for neural connections and synaptic pruning. They shape the foundation for future learning and cognitive abilities.
- Language development. Children in this stage experience a language explosion. They learn new words and expand their vocabulary. They start using more complex sentence structures. In this stage, children also begin to understand and express abstract concepts.
- Social and emotional development. Early childhood is a crucial time for the development of social skills. Children learn to interact with peers. They also engage in cooperative play and navigate their emotions. Kids develop empathy and understanding of others’ perspectives.

Middle Childhood Stage
The middle childhood stage is spanning from age six to twelve. It has significant physical, emotional, and cognitive changes. It differs from the early child development stage. These are some facts that you may include in your child development research paper:
- Physical growth and motor development. During middle childhood, children experience steady physical growth and maturation. They gain height and weight, and their coordination and motor skills improve. Activities such as sports, dance, and organized play contribute to their physical development.
- Cognitive development. Rapid cognitive development is crucial in middle childhood. Children become more logical and concrete in their thinking. It allows them to solve problems and understand abstract concepts more. Their memory, attention span, and information-processing abilities also improve.
- Academic achievement. Early childhood education research proves that academic achievement becomes important. Children develop skills in reading, writing, mathematics, and other subjects. They get a broader knowledge base and start to engage in more complex learning tasks.
- Social relationships and peer interactions. An increased focus on peer relationships characterizes middle childhood. Children develop the ability to form close friendships and engage in cooperative play. They gain a deeper understanding of social norms, empathy, and perspective-taking.

Adolescence
Adolescence is a crucial period of transition from childhood to adulthood. Child development and learning are different at this stage. Physical, emotional, and cognitive transformations mark it. Here’re th facts about this stage:
- Exploration and independence. Adolescence is a time of exploration and increasing independence. Individuals begin to question authority and establish their autonomy. Adolescents explore various interests, values, and beliefs. This is because they shape their own identities and make vital decisions.
- Physical transformation. Adolescence is a time of significant physical changes. It includes rapid growth spurts. Here individuals experience a surge in height and weight as their bodies mature. Secondary sexual characteristics also emerge during this stage.
- Emotional rollercoaster. Intense and fluctuating emotions mark the emotional landscape of adolescence. Hormonal changes can lead to mood swings and heightened emotional responses. Adolescents may experience a range of emotions. These emotions involve excitement, anxiety, and frustration. This is because they navigate the challenges of self-discovery and developing their identities.

When writing a child development research paper you need to focus on research, clear arguments and academic writing skills. But academic life can be so demanding that it’s hard to find time and effort to write a well researched and comprehensive paper. For students who are facing such challenges, buying research papers for sale can be a quick and reliable solution. These services offer papers written by experts to meet your academic needs and save you time.
By buying research papers you can get well written and structured content to use as a base or reference for your work. Whether you need help on topics like cognitive development, social interactions or parenting styles, these services allow you to customize research to your topic and submit a paper that meets academic standards and is on time.
15 More Child Psychology Research Paper Topics
So, here is a compilation of 15 thought-provoking child development research topics. They cover different stages and aspects of childhood development. These topics provide a rich foundation for further research in child development. You may use them to grab ideas on what to write about in your research!
- The Impact of Early Childhood Education on Cognitive Development: A Comparative Study.
- Analyzing the Influence of Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development.
- Examining the Interplay between Child Development and Education. Implications for Effective Teaching Strategies and Learning Outcomes.
- Unraveling the Multidimensional Aspects of Child Development. A Comprehensive Examination of Physical, Cognitive, Social, and Emotional Domains.
- The Impact of Research and Innovations on the Journal of Child Psychology.
- Parental Attachment and its Impact on the Psychological Development of Children.
- Examining the Effects of Divorce on Children’s Emotional Well-being and Change.
- The Relationship Between Bullying and Mental Health in School-aged Children.
- Understanding the Effects of Trauma on a Child Development: Implications for Intervention.
- Investigating the Effects of Gender Stereotypes on Children’s Career Aspirations.
- The Role of Executive Functioning in Academic Achievement in Middle Childhood.
- Exploring the Role of the Society for Research in Child Development in increasing knowledge.
- Early Childhood Research in Bridging the Gap between Theory and Practice.
- The Impact of Media on Body Image and Self-esteem in Children: A Cross-cultural Study.
- Understanding the Role of Cultural Factors in Shaping Moral Development in Children.
These child research topics provide a starting point for research in child psychology. You can use them to write research papers and deepen your knowledge of child development. These topics encompass various stages of childhood development. You can explore different aspects, such as cognitive, emotional, social, and moral development. Further research into these development research topics will contribute to your knowledge. You will enhance your understanding of its implications for education, parenting, and interventions. So, these child development topics for papers will be helpful for you. Good luck!
Now you have 35 topics to choose from and start writing. But before you do that, have a look at our sample essay that we have written below. It will give you a good idea on how a research paper is written and composed.
Here it is:
A Short Sample Essay on Why Play is Significant in Helping Children Learn and Understand Life
Play is more significant than you might think it is.
Play has a vital role in developing several aspects of a child. While it may seem nothing to you but science has shown that playing with kids or letting them play with toys, pets and even themselves, allows them to overcome physical and mental challenges. When children are playing, they learn to solve problems quickly, and can hone skills far better than those who don’t have the luxury to play. In this paper, you are going to see the benefits of play and why it’s significant in helping children learn and understand life.
Imaginative play is one of the most common aspects of a baby, which starts around at the age of 2. Everything that a child perceives, becomes his playing thing in his imagination. According to researchers, this is due to the fact that these imaginations become a recognition symbol. For example, a baby can see chunks of woods and imagine it to come into life and turn into a drum set or a boat. This makes a child’s brain work on its own bringing in new ideas.
This play allows children to understand that any object can actually transform in something better, hence, making them understand how the real-world works. While we may not notice how to play impacts a child in the early years, science has proven that it plays a vital role in the long-run.

With imaginative play, a child can understand the phenomenon of a superhero, a father or a police officer very easily. A baby experiments with identities and professions to explore different scenarios and outcomes that can take place during his/her life.
To be as simple as possible, imaginative play allows your child to have a sense of control because he becomes the master of interpreting the practices of the real-world and how everyday life works.
However, when a baby grows into a toddler, his play changes and becomes, what is known as, the parallel play. This helps children socialize with other children, creating story lines that are so complex that only they can understand.
It helps them understand what the terms like co-operation negotiation and sharing really is. According to Sara Wilford, director of the Art of Teaching Graduate Program at Sarah Lawrence College in Bronxville, NY, when children start to disagree with something and want to take decision, they start developing social skills.
Physical play on the other hand, allows children to have control over their bodies. By skipping, they can learn how to keep balance. Climbing monkey bars would allow their body to build strength and muscle. Sport activities, that involve groups, would help them understand coordination. Primary motor skills, such as running, pedaling, throwing etc. improve first before anything else. Fine motor skills, however, also start taking place at the age of 3, if the child is consistently being playful.
Physical play can also allow children to understand what stress and crankiness is. Your child likes to remain fit, which is why he demands a little physical play almost every hour or so (after the age of 3). This is because a child can become grumpy or tense if he hasn’t been active for an adequate amount of time. It may also cause the child to gain weight (unhealthy).
This play is so important that it helps them overcome mental challenges too. For example, if a baby can’t express a complex problem he’s going through; he will likely express it through physical play or would review it again and again until he finds a solution to it. This helps children overcome fear, and makes them independent.
Play also helps in creating independence and ingenuity in children. If a child is involved in multiple play routines, he/she will be able to dress and feed himself. Believe it or not, but research has shown that adults who have been more playful in their childhood, did better at school, at sports, jobs and pretty much everything.
These are the benefits that a child attains from play, which is why introducing playful habits and activities to a newborn child is very significant to improve child development.
Perfect! Since now you have read our first guide i.e. 12 facts for a research paper on child development and this one. It’s time to move to our final guide i.e. writer’s manual for research paper on child development, which along with our paper writers would help you to lay a strong foundation of how a research paper is beautifully composed and written.
Recommended reads
References:
- Geraldine French, (2007) – Children’s early learning and development, A Research Paper by the National Council for Curriculum and Assessment (NCCA) http://www.ncca.ie/en/curriculum_and_assessment/early_childhood_and_primary_education/early_childhood_education/how_aistear_was_developed/research_papers/childrens_learning_and_dev.pdf
- UNICEF, Early Childhood Development, The Key to Full and Productive Life. https://www.unicef.org/dprk/ecd.pdf
- Wisconsin Child Welfare Training System, Effects of Abuse & Neglect: A Focus on Typical Development. https://wcwpds.wisc.edu/childdevelopment/resources/CompleteDevelopmentDetails.pdf
- Dan Tynan and Christina Wood, (2016) – Amazing development facts about your child, Baby Development by BabyCenter. http://www.babycenter.com/big-story-child-development-fascinating-facts
- Aamodt, Sandra, and Sam Wang, (2011) – Welcome to Your Child’s Brain: How the Mind Grows from Conception to College. New York, NY: Bloomsbury.
- Nick Bilton, (2013) – The Child, the Tablet and the Developing Mind, The New York Times. http://bits.blogs.nytimes.com/2013/03/31/disruptions-what-does-a-tablet-do-to-the-childs-mind/?_r=1
- Mooney, Carol Garhart. 2000. Theories of Childhood: An Introduction to Dewey, Montessori, Erikson, Piaget, & Vygotsky. St. Paul, MN: Redleaf Press.


